Wired Connections
Copper Cables
Coaxial
- Cables need to be replaced from time to time as the insulation may degrade.
Unshielded twisted pair
- Copper cables are twisted around each other.
Fibre-optic cable
- Made of glass
- The digital data is transmitted in the form of light signals using the principle of total internal reflection.
Ethernet
- Ethernet is one of the most used technologies in LANs since the 1980s.
- LAN is used to interconnect devices using a wired medium such as UTP copper cables or fibre-optic cables, hubs and switches.
- This technology supports transmission rates of up to 100Gb/s
Ethernet Network
- An ethernet network is divided into various segments
- Network interface card and routers segment data into frames
- An error-checking mechanism is applied to the frames
- The receiver checks for errors in the frames, and in case of error, the sender is requested to resend the data packet.
Disadvantages of Ethernet
- Length of cabling is limited
- Limited size of segments results in more data packets, hence more collisions
- CSMA/CD is not optimal when a large number of devices are present in a network. Therefore, a network is segmented and more switches are used.
CSMA/CD
-
In an Ethernet network, if two data frames are transmitted at the same time, both frames may collide with each other resulting in errors
-
CSMA/CD is a technology incorporated into LANs to overcome this issue
-
In CSMA/CD the sender senses the channel before sending data frames. The data frames are only sent if the channel is sensed to be silent.
-
In case two senders transmit at the same time, collision occurs and the data corrupts.
-
In CSMA, the problem with the scenario is solved as the senders receive a corrupted form of data frame sent by them.
-
Then the senders wait for a random amount of time and resend the data
-
As the waiting time is different for both senders, data collision is avoided
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
-
A mechanism to detect errors in a data packet
-
Extra information is generated from the data using an algorithm such as a checksum
-
This checksum is added to the packet before transmission by the sender
-
When this packet is received by the receiver, it calculates the checksum using the same algorithm.
-
If the expected number is returned, there are no errors. If different numbers are returned, the packet will be resent.
Wireless Connectivity
- A wireless network uses radio signals to connect devices
Radio Transmission
- Radio signals are identified using their frequency
- Wi-Fi uses 2.4GHz and 5GHz
- The range of this signal is up to 20 metres. This range can vary with the thickness of a wall as the signal needs to pass through it.
Wi-Fi
- A computer requires a wireless network adaptor to connect to a wireless network
- A computer a long with a network interface controller is referred to as a station.
- All stations within a WAP share the same channel and are tuned to the frequency of a channel to receive transmissions.
2.4GHz waveband
- This waveband can be separated into different channels
- A channel is a communication link to send and receive data
- Many channels are adjacent to each other
- Adjacent channels may cause interference which leads to data corruption.
- There are typically only 4 “clear” bands on 2.4GHz
Performance of Wi-Fi systems
- A Wi-Fi access point shares its bandwidth among several devices. This might lead to poor performance.
- Performance of this system depends on the number of users and usage data.
CSMA/CA in Wireless Networks
-
Wireless networks use CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance) to allow nodes to transmit data at high speed and avoiding the collision of data frames at the same time.
-
Wireless stations are not capable of transmitting and receiving at the same time and hence, if a collision occurs during a transmission, it cannot be detected.
-
When a wireless node tries to send a data frame, it checks whether the channel is idle or not using CSMA/CA.
-
If the channel is idle, the data is sent. If the channel is busy, the node waits a random amount of time before checking the channel again. The mechanism is called a back-off mechanism and reduces the chances of collision.
-
The data frame is sent when the channel is sensed to be free.
-
After receiving the data frame, an acknowledgement is sent back to confirm that the data is received without any errors.
-
If the acknowledgement is not received within a specified amount of time, the data frame is sent again by the user.
Hidden Nodes Problem
- Hidden nodes problem is a scenario in which a node can communicate with the wireless access point, but cannot communicate directly with other nodes that are communicating with the access point.
- As a result, multiple nodes may send data to the access point at the same time leading to interference
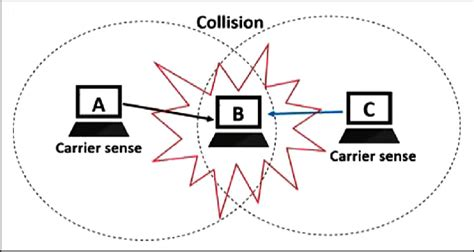
- In the example given, nodes A and C communicate with B (WAP) but are unable to communicate with each other.
Security in Wi-Fi systems
- Wireless networks are preferred for their ease of installation
- Security of data cannot be assured in this network
- Any device with a Wi-Fi facility will be able to receive data packets in that range of 20m.
- Therefore, it is important to secure data using encryption techniques.
WPA 2
- Uses AES to secure data.
- Password protection is enabled on the network.
- An SSID (Service Set Identifier) is used to identify an individual network (not WPA specific), disabling broadcasting can improve security.
Circuit Switching
-
This type of connection is used in traditional telephone networks. This type of switching does not allow other data packets to be transmitted during a connection session.
-
In case of circuit failure, the communication is disrupted. These disadvantages are overcome in packet switching.
-
An advantage of this is that data packets are sent serially.
-
Bandwidth is wasted if it isn’t being used
-
Sender and transmitter must talk at the same rate
-
If it breaks, a whole line needs replacing
Packet Switching
- A routing table contains information about the topology of the network. Using this information, a router forwards the packets to the next router using certain algorithms.
- In case a router is not available, the data packet is sent through another router.