Super Resolved Fluorescence Microscope
- Uses light
- Very high resolution (0.2nm)
- x1500 magnification
Advantages
- Stains that flouresce reveal different structures
- Good for viewing DNA + molecules
Disadvantages
- Some dyes interfere with cell parts
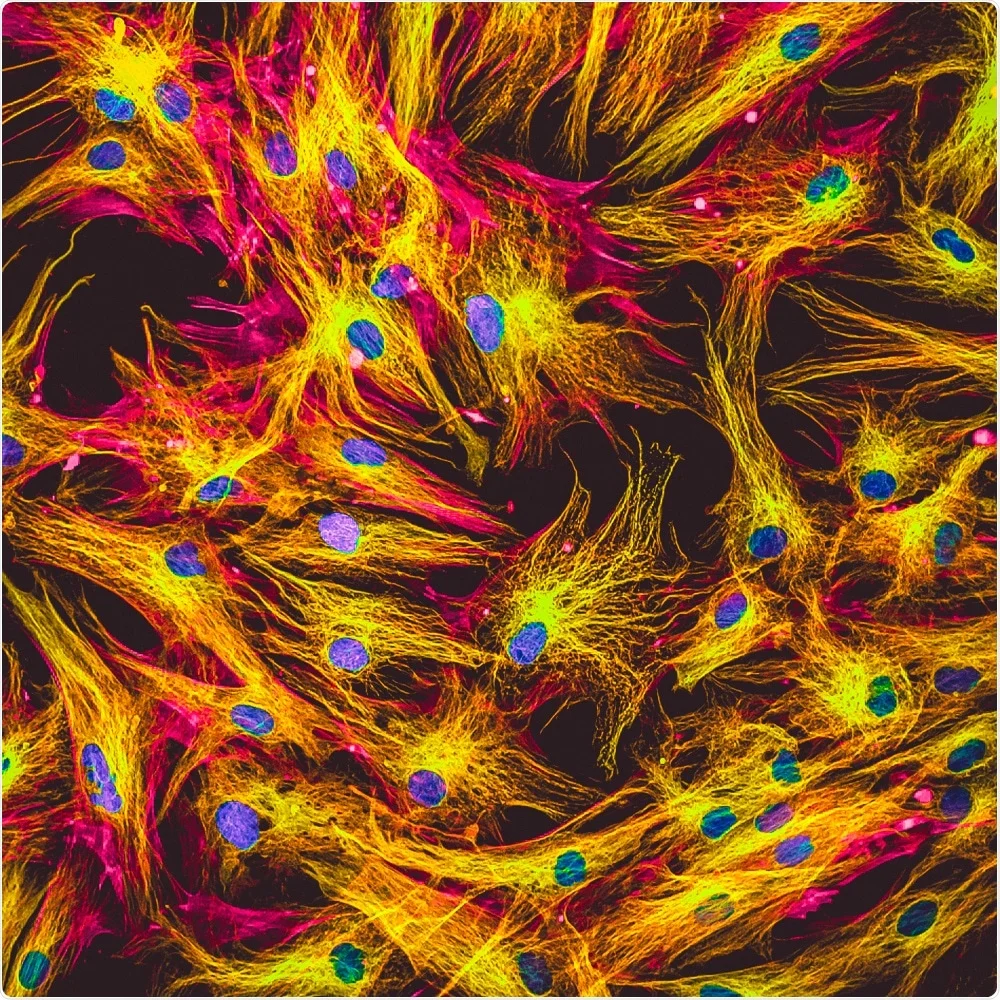
Laser Scanning (Confocal) Microscope
- Uses light
- 500nm resolution
- x1000 magnification
- Parts are labelled with a fluorescent dye.
Advantages
- Non-invasive clinical diagnosis
- 3D image overlays
Disadvantages
- Resolution limited by wavelength of light
- Dyes can interfere with cell function

Atomic Force Microscope
- ”Feels” surface of specimen
- Uses light via a laser diode
- 0.1nm resolution
- x100 000 000 magnification
Advantages
- Normal cell conditions
- Living systems
- Drug interactions
Disadvantages
- Can’t see inside cells, surface only

Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- Magnification up to x2000000
- 2D greyscale image
- Resolution of 0.5nm
Advantages
- Seeing ultra structure
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Large
- Prone to artifacts
- Samples will be killed

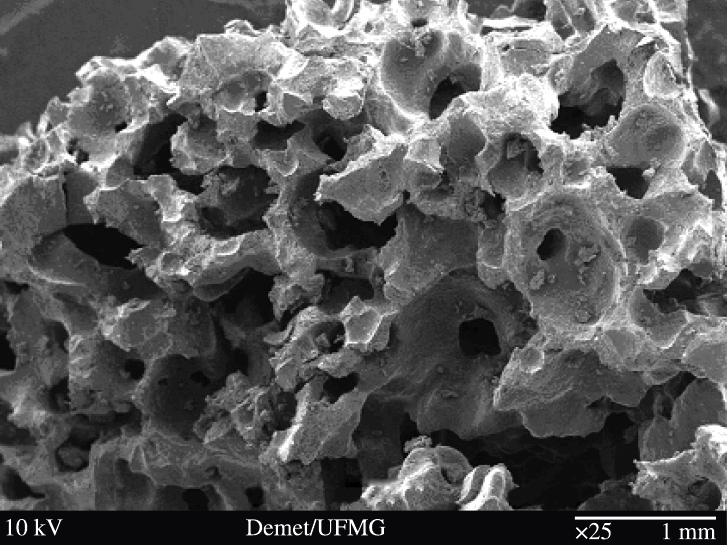
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Magnification between
x15andx200000 - Resolution between
3nmand10nm - Sample kept in vacuum
Advantages
- 3D image
- Good for organism appearance
Disadvantages
- Very large
- Expensive
- Samples dead
- Salt stains are dangerous
- Requires training
