NOT XOR
000 011 101 111
NOT A OR B AND C
OR 0 1 1 1
NAND 1 1 1 0
Adders and flip-flops
Half adder
-
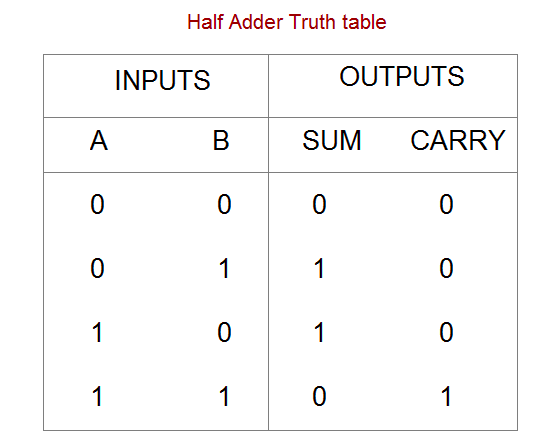
The ALU in a CPU uses a half-adder logic circuit for performing the binary addition of two bits.
-
The input consists of two bits, A and B, and hence 2^2=4 input combinations are possible.
-
Two output bits are required to denote the sum and the carry.
-
The output Sum(S) is 1 when both inputs A and B have different values.
-
S is true under two conditions:
- A is false and B is true
- A is true and B is false
-
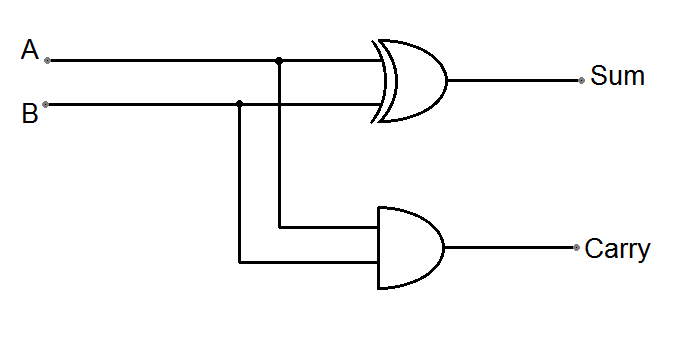
The Sum is an XOR operation between A and B.
-
The output carry is only 1 when A and B are also true
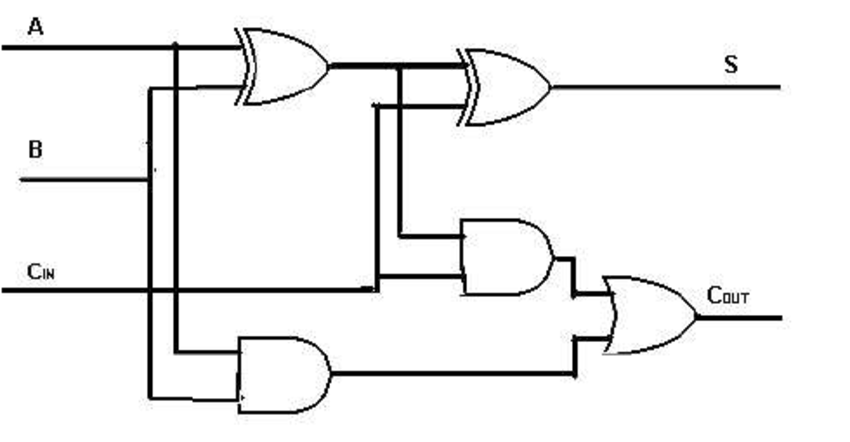
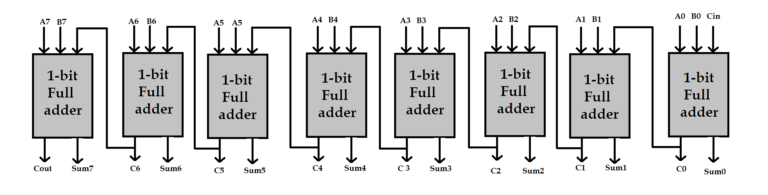
Full Adder
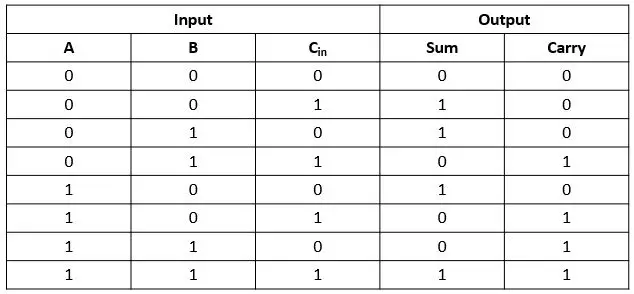
Expanding full adders
- Full adders can be expanded to adders of any number of bits.
- n full adders shall be combined to form an n-bit adder.
Combinational vs Sequential Circuits
Combinational circuit
- The output is dependent on the combination of inputs.
Sequential Circuit
- The output is not only dependent on the present state of input variables, but also on the past state of output variables.
- To store the past state of input variables, we need a memory unit in the circuit.
Recall
- Two bits in, 1 bit out and 1 carry out (half) - A AND B in → S AND C out
- Two bits in, 1 bit out and 1 carry out (full) - A AND B AND C in → S AND C out
- AND
- NOR
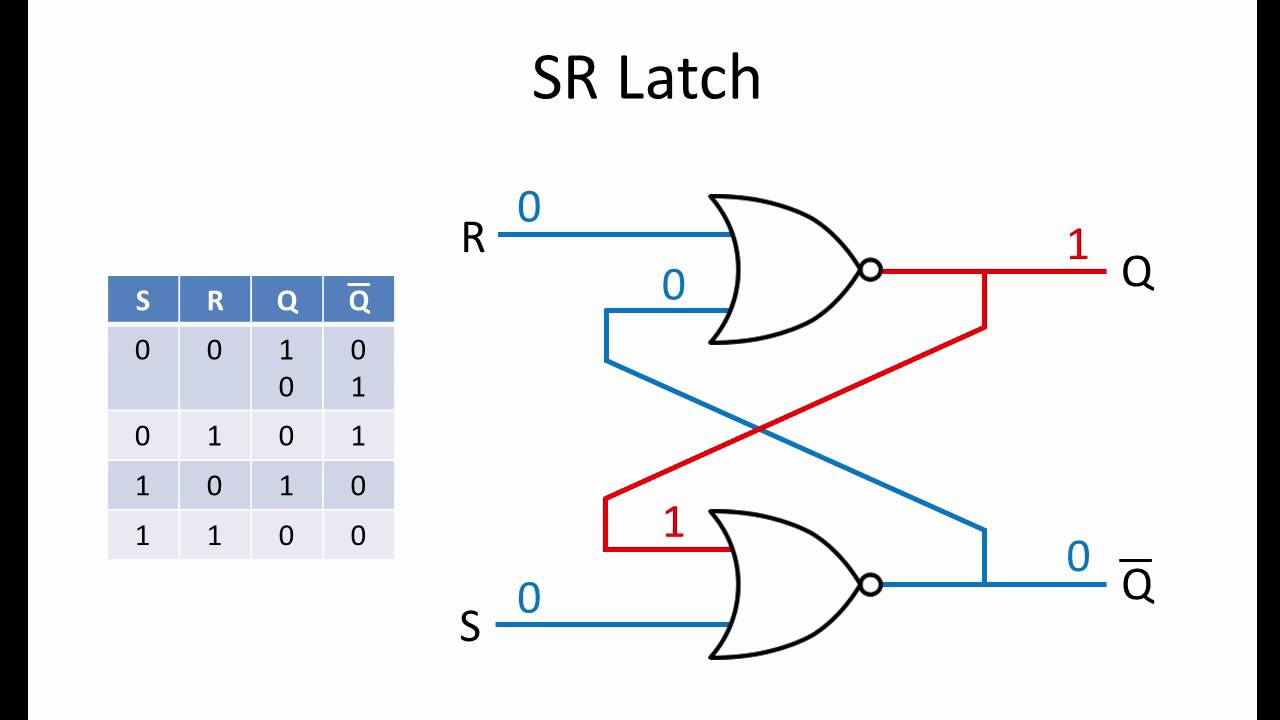
SR Latch
- The circuit diagram and truth table for an SR latch.
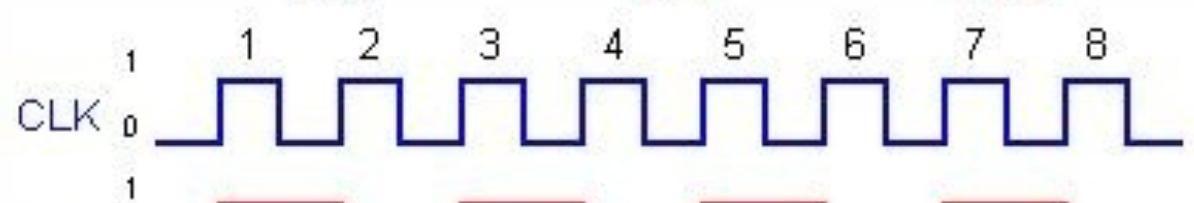
Sequential Circuits - Clock
- For synchronous sequential circuits, we require a clock signal.
- A clock is a type of sequential circuit that changes state at regular intervals.
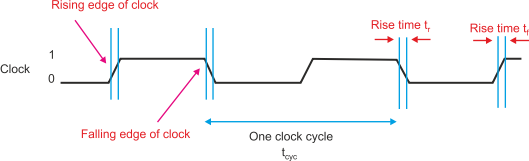
- A clock signal synchronises the components in sequential circuit. A positive-edge triggering clock signal is given below. The output responds to the changes in the input only at the positive edge of the clock pulse.
Falling Edge
- Alternatively, a negative-edge triggering sequential circuit can also be designed.
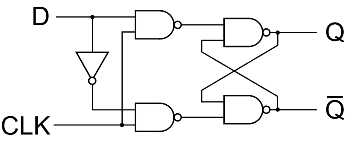
D flip-flop
Requires the clock pulse.
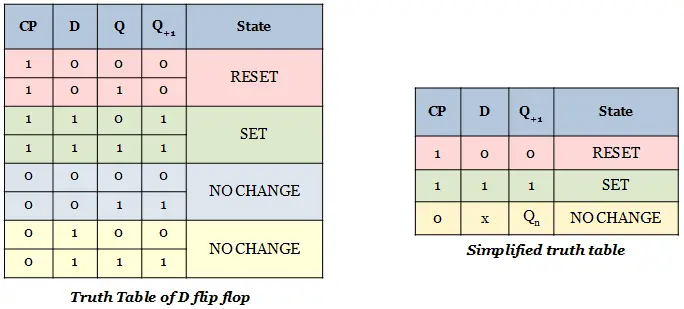
- The input and output waveforms of a positive-edge triggered D flip-flop are given.
- The output Q follows the input D at the positive edges of the clock pulse.
- Assume the value of Q is 0 initially.
D = Delay
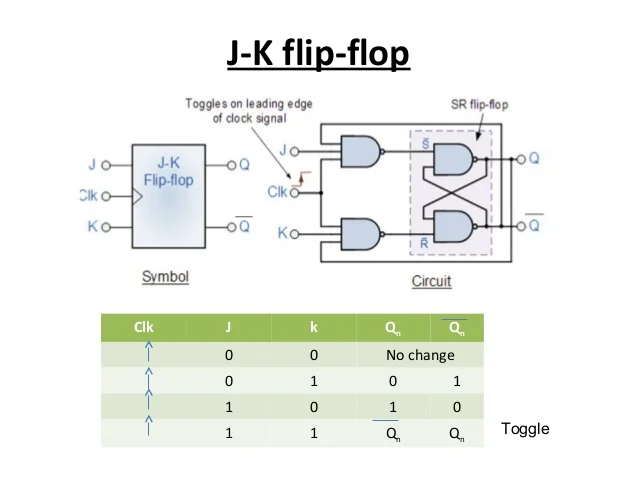
JK Flip Flops
- The input J acts as the set input and K acts as the reset input. When both J and K are equal to 1, the value of Q is switched.