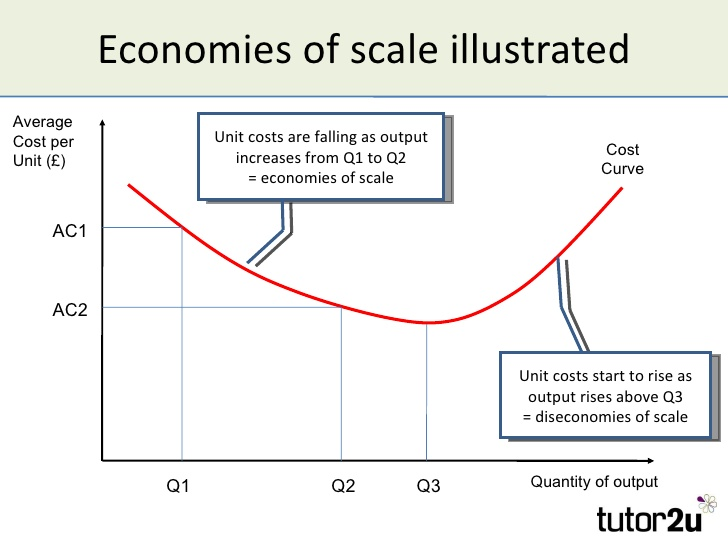
Economies of scale arise when unit costs fall as output increases.
Internal Economies of Scale
- Buying economies—buying greater quantities usually results in lower price (bulk-buying)
- Technical—use of specialist equipment of process to boost productivity
- Marketing—spreading a fixed marketing spend over a larger range of products, markets, and customers
- Network—adding extra customers or users to a network that is already established
- Financial—larger firms benefit from access to more and cheaper finance
Labour Productivity
Labour Productivity = Output per period (units) / Number of employees at work
The answer will typically be expressed in terms of output per employee. Eg: 1000 units per employee per month