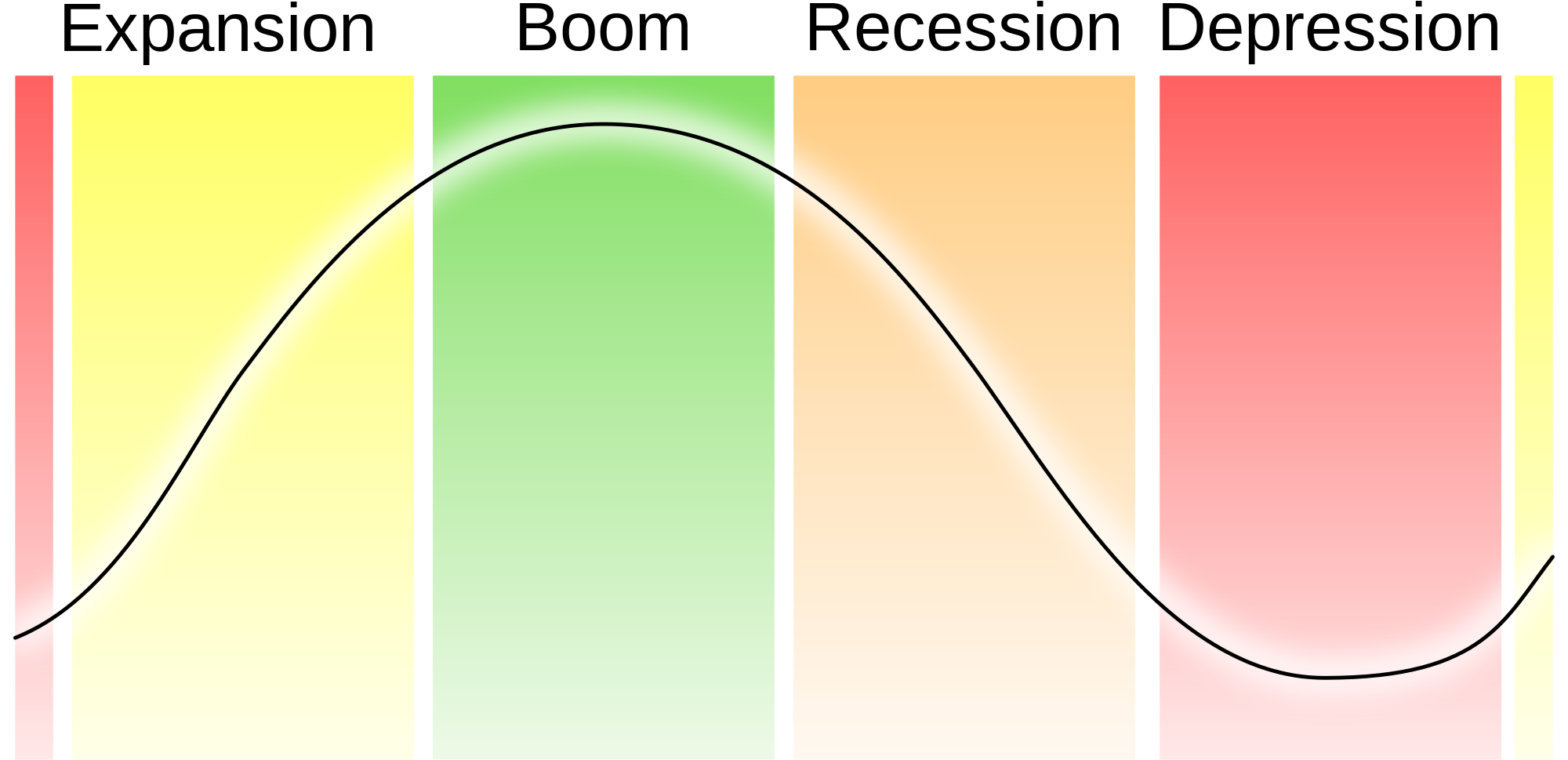
- Economic activity and economic growth are measured by GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
- The market value of all goods and services produced within a country.
Key Factors Affecting Short-term Economic Growth
- Interest rates set by the central bank
- Fiscal policy – government spending and taxation
- Commodity prices such as oil, gas and foodstuffs
- Exchange rates
- Trading conditions in other countries
- Confidence of businesses and households
Economic and Social Costs of Growth
-
High rates of GDP growth can bring about undesirable economic and social costs - much depends on the nature of growth
-
Risks of higher inflation and higher interest rates
- Fast-growing demand can lead to demand-pull and cost-push inflation - this leads to a conflict between macro objectives
- The central bank may decide to raise interest rates to control inflation
-
Environmental effects
- More negative externalities such as pollution & waste
- Risk of unsustainable extraction of finite resources - ie, fast growing countries may cause a long-run depletion of natural resources
-
Inequalities of income and wealth
- Rapid increases in real national income can lead to a higher level of inequality and social divisions
- Many of the gains from growth may go to only a few people