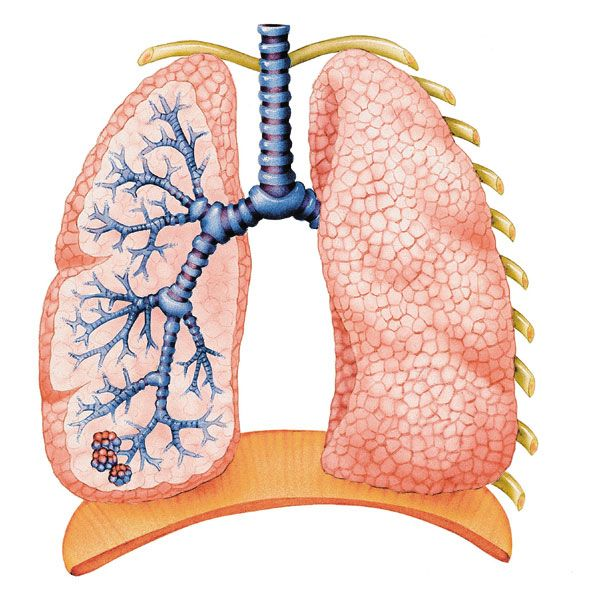
 Alveoli are the sole site of gaseous exchange.
Alveoli are the sole site of gaseous exchange.
Adaptations for gaseous exchange
Gaseous Exchange
movement of gases by diffusion between an organism and its environment.
- large surface area : many alveoli
- short distance for diffusion: alveoli and capillary wall are one cell thick (squamous epithelium)
- steep diffusion gradient: ventilation and good bloody supply
- semi-permeable membrane: cell membranes are permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide
Alveoli
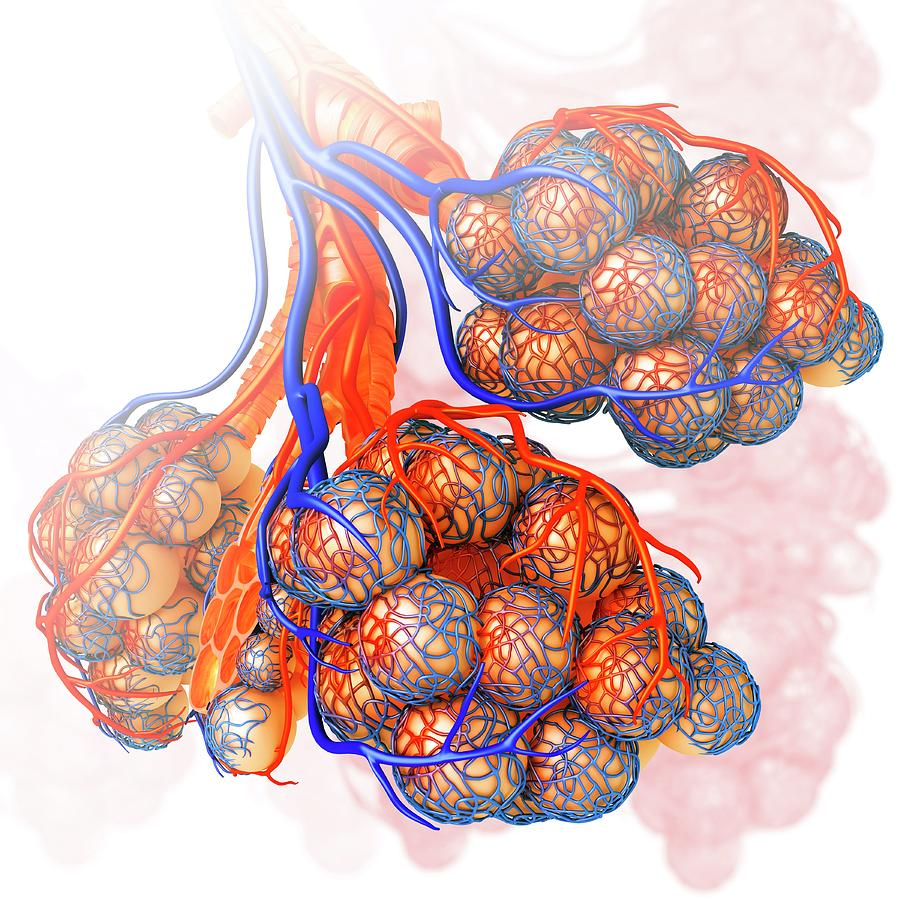 Blue blood is arriving to be oxygenated and red blood is leaving after being oxygenated.
Blue blood is arriving to be oxygenated and red blood is leaving after being oxygenated.
Alveoli have thin walls and provide large surface areas for gas exchange.
Tissue and function distribution in the human lungs
Requirements of human airways
- flexible
- divide many times, allow air to reach alveoli
- high elasticity (stretch & recoil)
- strong, to prevent collapse
Components
Trachea
- much of the wall is cartilage
- prevents collapse when air pressure is low
- Contains:
- elastic fibres: recoil & return
- smooth muscles: constrict airway
- blood vessels: supply cells with nutrients and remove waste
- Innermost lining is epithelium (ciliated and goblet cells)
Bronchi
- Same as trachea, just smaller
Bronchioles
- Larger ones may have some cartilage
- Mainly smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Alveoli
- Squamous epithelium
- elastic fibres: recoil after exhalation to prevent bursting