- Change management is an aspect of management focusing on ensuring that the business responds to the environment in which it operates
- Four key features of change management
- Change is the result of dissatisfaction with present strategies
- Essential to develop a vision for a better alternative
- Necessary to develop strategies to implement change
- There will be resistance to change
Internal Causes of Change
- Arise from factors within the control of the business
- Decisions taken by management
External Causes of Change
- Arise from factors outside the control of the business
- As a result of changes in the external environment
Forces for change
Internal forces
- Desire to increase profitability
- Reorganisation to increase efficiency
- Conflict between departments
- To change organisational culture
External forces
- Customer demand
- Competition
- Cost of inputs
- Legislation and taxes
- Political
- Ethics and social values
- Technological change
Incremental vs Radical Change
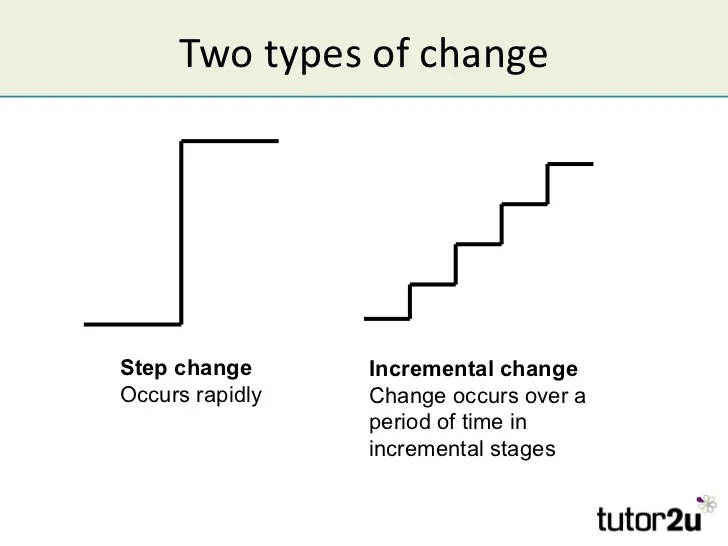
Incremental
- Small adjustments made gradually
- Usually over a long period of time
- Changes in order to reach a particular goal
- Does not alter working practices in any significant way
Radical (step change)
- A way to achieve the same goal but in a much shorter time
- Has a significant effect and long-term effects on workplace practice
- Requires careful management of the change process
- Can have significant and distressing impact on employees
Disruptive change
- An irreversible change to products, processes and markets; a change that alters the future completely from what it was before.
- Disruptive innovation helps create new markets and disrupts existing markets.
Examples
- Media Streaming
- Netflix
- YouTube
- Spotify
- Amazon Prime
- Grocery Retailing
- Ocado
- Graze
- Amazon Pantry
- Travel and Accomodation
- Expedia
- TripAdvisor
- Airbnb
- Fashion Retail
- Consumer file storage
- Dropbox
- Google Drive
- Microsoft OneDrive
- Apple iCloud
